Semaglutide Weight Loss Dosage Chart is an injectable glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, originally approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating type 2 diabetes under the brand names Ozempic and Rybelsus. In recent years, however, semaglutide has garnered significant attention for its potential in aiding weight loss in individuals with obesity, even those without diabetes. The FDA has approved a higher-dose version of semaglutide, branded as Wegovy, specifically for chronic weight management. This article delves into the science behind semaglutide, its effectiveness in weight loss, its mechanism of action, and the potential implications for obesity management.
Buy Semaglutide for Weight Loss Here >>
Obesity is a complex, chronic disease affecting millions worldwide. Its causes range from genetic factors and lifestyle choices to environmental influences. Despite a growing understanding of the underlying mechanisms of obesity, managing this condition has remained a challenging task. Traditional methods such as diet and exercise often prove insufficient for long-term weight loss in many individuals. This has led to the development of pharmaceutical interventions aimed at helping people manage their weight more effectively. Among the most promising of these treatments is semaglutide, a medication initially designed to manage type 2 diabetes but now making headlines for its efficacy in promoting weight loss.
Semaglutide Dose for Weight Loss
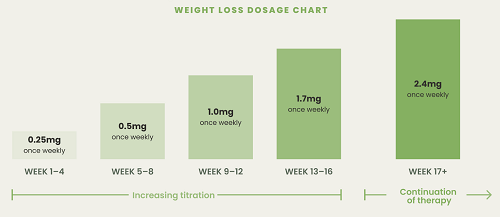
For weight loss, semaglutide is typically prescribed in a higher dose under the brand name Wegovy. The approved dose for weight management is 2.4 mg injected once weekly. The dosing schedule involves a gradual increase to minimize potential side effects such as nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort. Here’s how the typical dosing regimen works:
- Initial dose: 0.25 mg once weekly for 4 weeks
- Step-up dose: 0.5 mg once weekly for 4 weeks
- Subsequent increases: 1 mg, 1.7 mg, and finally 2.4 mg once weekly over several weeks.
This gradual escalation helps the body adjust to the medication, reducing the likelihood of side effects. Once the 2.4 mg maintenance dose is reached, the patient continues to take this dose weekly for long-term weight management.
This dosing regimen is designed to be combined with lifestyle modifications such as a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity for the best results.
Buy Semaglutide for Weight Loss Here >>
The Mechanism of Semaglutide
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, a class of drugs that mimic the effects of the naturally occurring hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). GLP-1 is secreted by the intestines in response to food intake and plays several roles in regulating glucose metabolism and appetite control.
- Glucose Metabolism: GLP-1 helps lower blood sugar levels by enhancing insulin secretion from the pancreas, especially in response to elevated glucose levels. It also inhibits the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar by prompting the liver to release stored glucose. This dual action makes semaglutide particularly effective in managing blood sugar levels for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Appetite Suppression: Beyond its effects on glucose, GLP-1 also influences appetite regulation. It slows gastric emptying (the rate at which food leaves the stomach), which prolongs the feeling of fullness after eating. Additionally, GLP-1 acts on receptors in the brain, particularly in areas related to hunger and satiety, such as the hypothalamus, to reduce food intake.
By leveraging these mechanisms, semaglutide can help individuals not only regulate their blood sugar levels but also reduce their caloric intake, ultimately leading to weight loss.
Clinical Trials and Evidence
The efficacy of semaglutide for weight loss was first demonstrated in a series of large-scale clinical trials, collectively known as the STEP (Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity) trials. These trials evaluated the impact of semaglutide on weight reduction in individuals with obesity or overweight, with or without type 2 diabetes.
- STEP 1 Trial: In this pivotal trial, nearly 2,000 adults with obesity (but without diabetes) were randomized to receive either semaglutide (2.4 mg once weekly) or a placebo for 68 weeks. Participants in the semaglutide group lost an average of 14.9% of their body weight, compared to 2.4% in the placebo group. A significant proportion of individuals in the semaglutide group achieved weight reductions of 10% or more, a threshold often associated with meaningful improvements in metabolic health.
- STEP 2 Trial: This trial focused on individuals with type 2 diabetes. Over the 68-week study period, participants receiving semaglutide experienced a 9.6% reduction in body weight, compared to 3.4% in the placebo group. Although the weight loss observed in this trial was less pronounced than in the STEP 1 trial, likely due to the metabolic complexities associated with diabetes, the results were still impressive and clinically meaningful.
- STEP 3 and STEP 4 Trials: These studies reinforced the findings from STEP 1 and STEP 2, confirming that semaglutide leads to sustained, clinically significant weight loss in a broad range of patients, regardless of their diabetes status. Importantly, these trials also highlighted the long-term benefits of continued semaglutide use, with participants maintaining much of their weight loss over extended periods.
Buy Semaglutide for Weight Loss Here >>
FDA Approval and Indications
In June 2021, the FDA approved Wegovy (semaglutide 2.4 mg) for chronic weight management in adults with obesity or overweight, in conjunction with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity. Specifically, Wegovy is indicated for adults with a body mass index (BMI) of:
- 30 kg/m² or greater (obesity), or
- 27 kg/m² or greater (overweight) with at least one weight-related comorbidity, such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes, or dyslipidemia.
The approval of Wegovy marked a significant milestone in the treatment of obesity, offering a new option for individuals who struggle to achieve meaningful weight loss through lifestyle changes alone. Importantly, semaglutide’s approval also reflects a broader shift in the medical community’s approach to obesity, recognizing it as a chronic, relapsing condition that often requires long-term management with pharmacotherapy.
How Semaglutide Compares to Other Weight Loss Medications
Several medications are currently approved for weight loss, including liraglutide (Saxenda), another GLP-1 receptor agonist, as well as phentermine/topiramate (Qsymia), bupropion/naltrexone (Contrave), and orlistat (Xenical). While these drugs can promote weight loss, they often come with limitations such as modest efficacy, safety concerns, or tolerability issues.
Semaglutide stands out for several reasons:
- Greater Efficacy: Compared to other weight loss medications, semaglutide has demonstrated superior weight loss outcomes in clinical trials. For example, liraglutide, the closest comparator, typically produces 5-7% weight loss, compared to the 15% or more seen with semaglutide in some cases. This makes semaglutide one of the most effective pharmacologic treatments for obesity currently available.
- Convenience: Semaglutide Weight Loss Dosage Chart is administered via a once-weekly subcutaneous injection, offering greater convenience than daily injections or oral medications. This dosing schedule may improve adherence and contribute to its effectiveness in real-world settings.
- Safety Profile: Although semaglutide is generally well-tolerated, it can cause gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, particularly when treatment is initiated or doses are increased. However, these side effects are usually transient and can be managed by adjusting the dose or using supportive treatments. Importantly, semaglutide has not been associated with the same cardiovascular risks seen with some older weight loss medications, making it a safer option for long-term use.
Buy Semaglutide for Weight Loss Here >>
Side Effects of Semaglutide
Like all medications, semaglutide is not without its risks. The most common side effects reported in clinical trials include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Abdominal pain
These gastrointestinal symptoms are usually mild to moderate and subside with continued use. Gradual dose escalation helps mitigate these effects. In rare cases, more severe adverse effects can occur, such as pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) or gallbladder disease. Individuals with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 should avoid using semaglutide due to potential risks.
Implications for Obesity Treatment
The advent of semaglutide as a weight loss medication marks a significant turning point in the management of obesity. Historically, many clinicians and patients viewed obesity as a condition that could be overcome solely through lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise. However, a growing body of evidence suggests that for many individuals, especially those with severe obesity, such changes are often insufficient due to the complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors that drive weight gain and hinder weight loss.
Semaglutide offers a pharmacological tool that can help bridge the gap between lifestyle interventions and bariatric surgery, providing a middle ground for individuals who may not qualify for surgery or are hesitant to pursue such invasive treatments. In clinical practice, semaglutide is often used as part of a multimodal approach to obesity management, alongside dietary counseling, exercise programs, and behavioral therapy.
Buy Semaglutide for Weight Loss Here >>
Future Directions and Research
While semaglutide’s approval for weight loss is a major breakthrough, research is ongoing to explore its full potential and refine its use. Several areas of interest include:
- Long-Term Outcomes: While clinical trials have demonstrated the short- to medium-term efficacy of semaglutide for weight loss, further research is needed to understand its long-term effects, particularly with regard to maintaining weight loss and preventing weight regain after discontinuation.
- Combination Therapies: Researchers are investigating the potential benefits of combining semaglutide with other medications or interventions to enhance weight loss outcomes. Early studies suggest that combining GLP-1 receptor agonists with other weight loss drugs, such as tirzepatide, another novel diabetes medication with dual action on GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), may lead to even greater weight reductions.
- Expanded Indications: While semaglutide is currently approved for weight loss in individuals with obesity or overweight, future studies may explore its use in broader populations, such as individuals with a lower BMI who have obesity-related health risks or specific metabolic conditions.
Semaglutide Dosage for Weight Loss
Semaglutide represents a paradigm shift in the treatment of obesity, offering a highly effective, well-tolerated pharmacologic option for individuals struggling with weight management. Its dual action on appetite regulation and glucose metabolism makes it particularly suited for people with obesity, regardless of whether they have type 2 diabetes. With its promising results in clinical trials and a growing body of real-world evidence, semaglutide has the potential to transform the landscape of obesity treatment, offering hope to millions of individuals worldwide who have struggled to lose weight through traditional methods.
As research continues to evolve, Semaglutide Weight Loss Dosage Chart may become a cornerstone of obesity management, ushering in a new era of evidence-based, personalized care for this complex and challenging condition.